
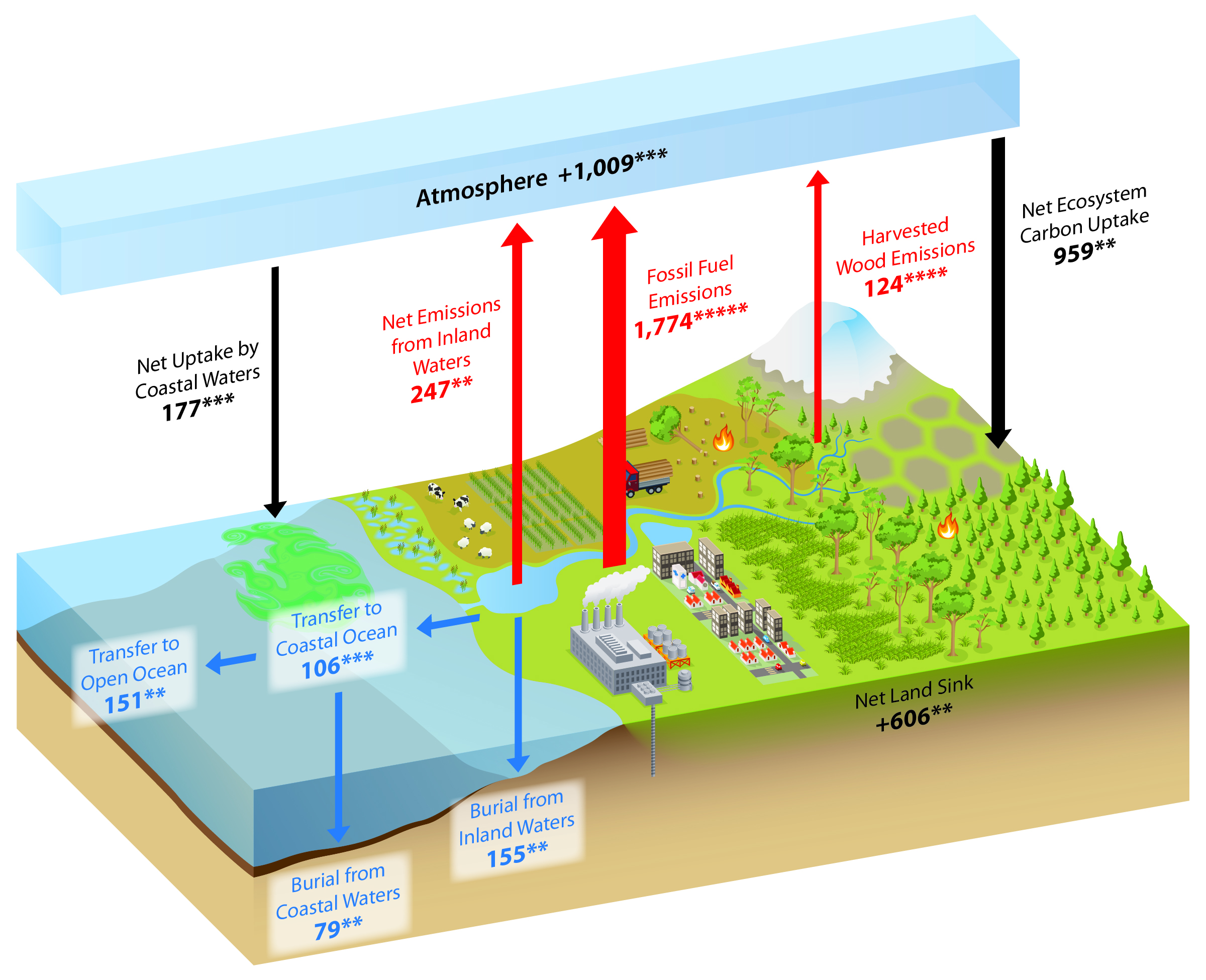
Such measurements indicate how much carbon is taken up by ocean biology. MODIS measures chlorophyll concentrations and fluorescence at the ocean surface to assess the concentration and health of photosynthesizing organisms like phytoplankton. Since Terra measurements begin in 2000, they provide a record of the rate and extent of change for more than a decade. Terra also measures concentrations of carbon monoxide in the atmosphere. All four measurements are necessary to estimate how much carbon plants take up as they grow, and how much is being released to the atmosphere over time. Terra’s five instruments provide measurements of plant (vegetation) composition, structure, extent, and change. If, on the other hand, warming slows plant growth, habitats will shift and more carbon will go into the atmosphere where it can cause additional warming. If more plants grow, they will take more carbon out of the atmosphere and cool temperatures. For example, plants may bloom earlier in the year and grow for more months (assuming sufficient water is present) as the growing season gets longer, altering the food supply for animals in the ecosystem. As ecosystems change under a changing climate, the carbon cycle will also change. Because plants and animals are an integral part of the carbon cycle, the carbon cycle is closely connected to ecosystems. The carbon returns to the atmosphere when the plants decay, are eaten and digested by animals, or burn in fires. Plants on land and in the ocean convert carbon dioxide to biomass (like leaves and stems) through photosynthesis. On the short time scale, the carbon cycle is most visible in life. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land, ocean, and life through biological, chemical, geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle. Because some carbon gases are greenhouse gases, changes in the carbon cycle that put more carbon in the atmosphere also warm Earth’s climate. It is one of the primary building blocks of all organic matter on Earth and a key element in setting Earth’s temperature. Carbon is a fundamental part of the Earth system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
